Deep Learning Part 1 - What's Deep Learning?
Deep Learning Part 1 - What is Deep Learning?
This will be part of a series of posts for my own reference and continued professional development in deep learning. It should mostly follow important points taken from François Chollet’s book Deep Learning with Python, Second Edition.
The main book itself can be found at Manning.com
Create the environment
Book was made with tensorflow 2.6
#Running a custom runtime with anaconda
#(base) conda install nb_conda_kernels
# conda create --name deep-learning
# conda activate deep-learning
# conda install ipykernel
# conda install tensorflow==2.6 keras==2.6
#Here in Jupyter, menu>Kernel>Change kernel>conda env:deep-learning
No code should be required for this chapter, it will mostly be covering high-level definitions, history of machine learning, and why it’s so popular.
- Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning, which is itself a subset of Artificial Intelligence
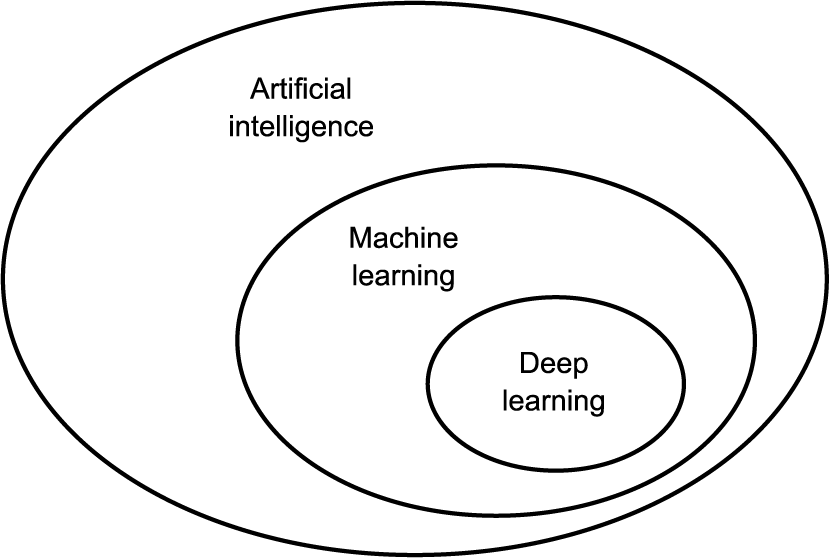
AI
-
Generally, AI is a field that is trying to imitate capabilities that were previously only able to be performed by humans.
-
It encompasses machine learning because it includes software that is hard-coded instructions such as early chess-playing programs. These hard-coded rulesets manipulating information is called symbolic AI. These computers with specialized skills were also called expert systems.
-
These approaches were good for logical problems but not for problems with less defined rules.
Machine Learning
-
Early computer practictioners felt computers could only help humans do what humans know how to do. Did not creativity or learning from experience. Practitioners felt computers could only do what they were explicitly told to accomplish.
-
Alan Turing in the 1940’s/50’s posited the Turing test, or the ability of a computer to mimic a human in cognitive capabilities.
- Machine Learning turns typical computer programming upside down
- Traditional programming gives a computer rules to operate on the input
- Machine Learning gives the computer data, the associated answers, and it is trained to learn the rules
-
Machine Learning (ML) has seen increased use since we have better hardware and larger datasets.
-
ML is related to statistics in the same way medicine is related to chemistry. Yes, it uses it, but it cannot be reduced completely to that level.
- ML needs 3 things:
- Input data
- Expected Output
- A method of measuring error or how well the method is doing it’s job
“So that’s what machine learning is, concisely: searching for useful representations and rules over some input data, within a predefined space of possibilities, using guidance from a feedback signal. This simple idea allows for solving a remarkably broad range of intellectual tasks, from speech recognition to autonomous driving.” -François Chollet
Deep Learning
-
Deep learning wants to take the data representation game to a whole new level. In fact, multiple levels. The “Deep” in “Deep Learning” is referring to the deepness of the layers and levels of representation of the data which comes from employing multiple layers of neurons.
-
It’s not very useful to anthropomorphize deep learning networks as minds that work like ours.

-
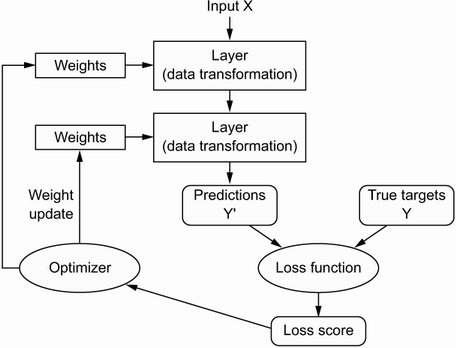
The representation of each layer is held in the weighting of the connection between each input and each output between the layers. The weights can be called the parameters. This is different from hyperparameters which are larger macro-level settings such as regression weight, learning rate schedule/policy, etc.
-
To see how well the goal is being approached, the measure of performance is called the loss function - it can also be called the objective function or cost function. The scoring can be considered the distance the current model is from the answer. ML practictioners use this score as a feedback signal to adjust the weights of the neural network.
Deep Learning Successes
- Near-human-level image classification
- Near-human-level speech transcription
- Near-human-level handwriting transcription
- Dramatically improved machine translation
- Dramatically improved text-to-speech conversion
- Digital assistants such as Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa
- Near-human-level autonomous driving
- Improved ad targeting, as used by Google, Baidu, or Bing
- Improved search results on the web
- Ability to answer natural language questions
- Superhuman Go playing
-François Chollet
Reasonable Expectations
- Don’t expect Human-level general intelligence in the next 10-20 years.\
- AI has had huge hype cycles before and it resulted in failed dreams and dried up investment.
- We’ll get there eventually, but it’s going to take awhile
Deep Learning isn’t the only Tool
- Deep Learning requires a lot of data
- Other tools in the ML toolbox may be a better fit for the problem
Perhaps check out the list of ML approaches
Deep Learning was enabled by Advances
- Figuring out the backpropogation (backprop) algorithm
- Implemented backprop via gradient descent
-
Has only really been around for 10 years, since the ImageNet breakthrough in 2012.
-
Deep convolutional neural networks (convnets)
-
Deep learning makes problem-solving much easier because it automates feature engineering. This used to be extremely difficult and required a lot of expert knowledge.
-
The ML landscape is dominated by deep learning and gradient boosted trees. Keras and Tensorflow are common implementations.
-
Gradient boosted trees is used for problems where structured data is available, whereas deep learning is used for perceptual problems such as image classification.
-
Deep learning is experiencing rapid growth due to the explosion of data from the Internet and the incredible parallel computing capabilities that Graphical Processing Units (GPUs) from the gaming industry brought forth.
-
Current state of the art training is completed on high end GPUs and Tensor Processing Units (TPUs)
- Algorithms have improved drastically, critically, the capability to conduct backprop without losing the signal throughout the layers of the neural net. This was enabled via:
- Refined activation functions
- Better optimization schemas such as Adam which you see all the time.
- More advanced methods to improve gradient propagation include batch normalization, residual connections, and depthwise separable convolutions.
Deep Learning Should Continue
Deep learning has on its side the following advantages:
- Simplicity
- Scalability
- Versatility
- Reusability